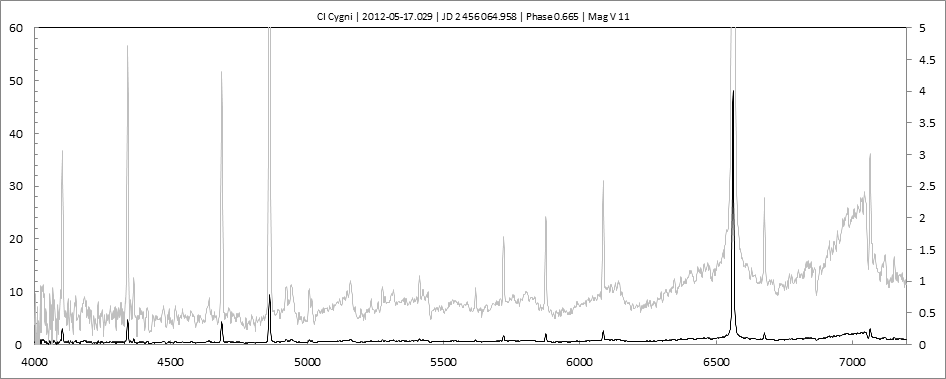
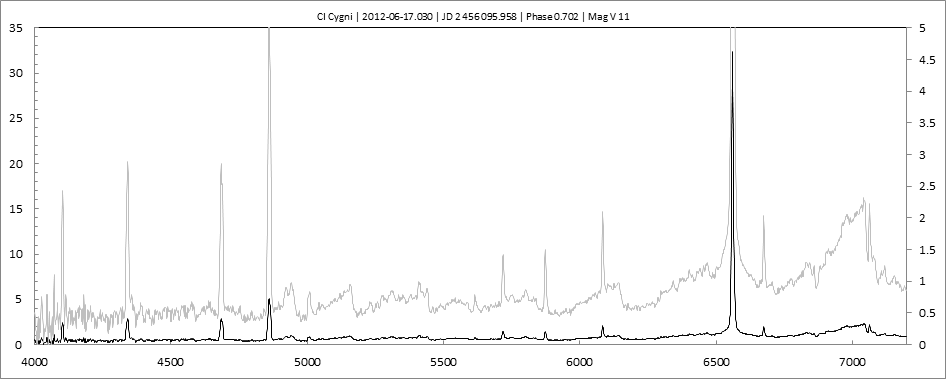
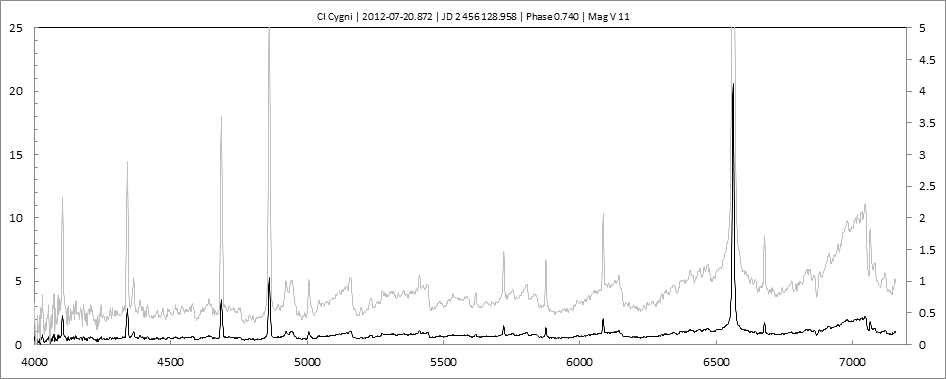
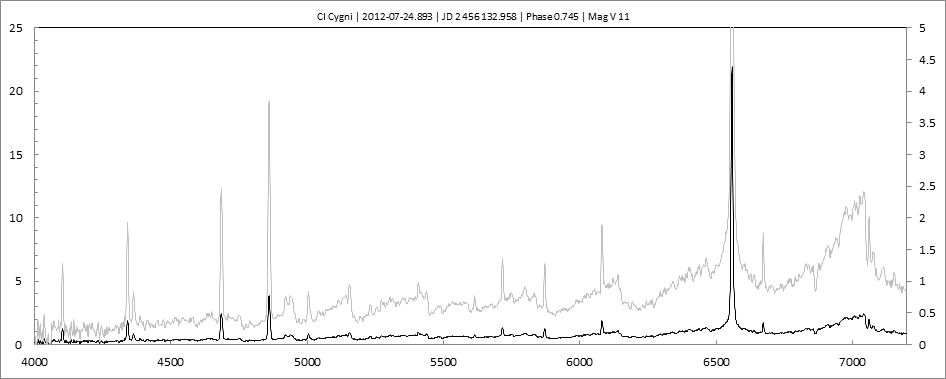
Projets Spectroscopie 1
Etoiles Symbiotiques
CI Cygni
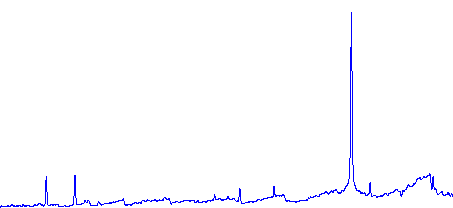
![]()
2010 Outburst |
|---|
AD [2000] DE [2000] Mag P Orb [j] Spec CI Cygni est une symbiotique particulière à plus d'un titre :
- symbiotique de forte excitation : [Fe VII], [Ne III], [NeVII], HI, He I, He II , [O III]
- l'une des rares étoiles symbiotiques dans lesquelles a été mis en évidence un disque d'accrétion. L'étoile géante emplit son lobe de Roche, caractéristique rare pour une étoile symbiotique.
- sa courbe de lumière présente des éclipses.
CI Cygni est entrée depuis 2008 dans une phase d'outbursts, qui semble similaire à celle qu'elle a connu entre 1971 et 1979.
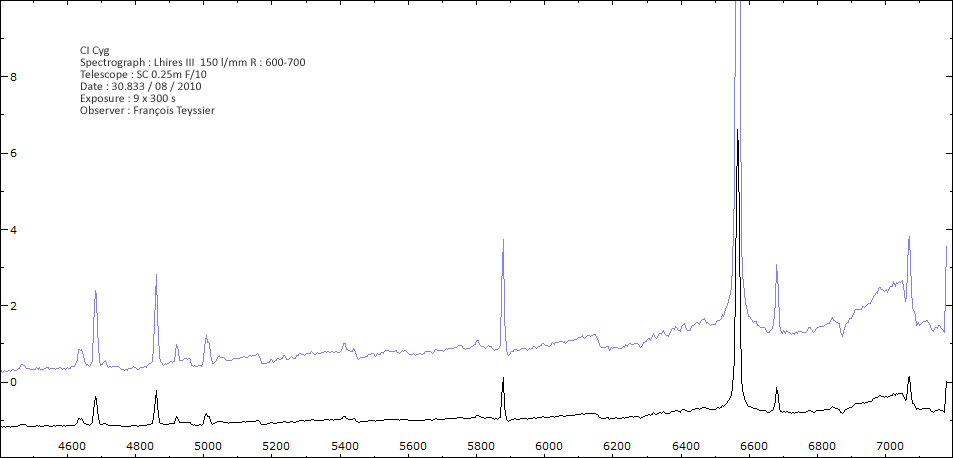
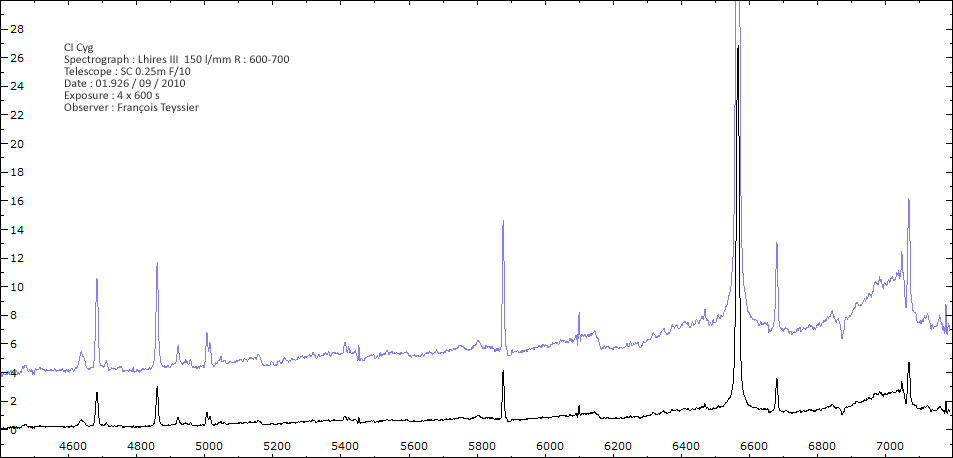
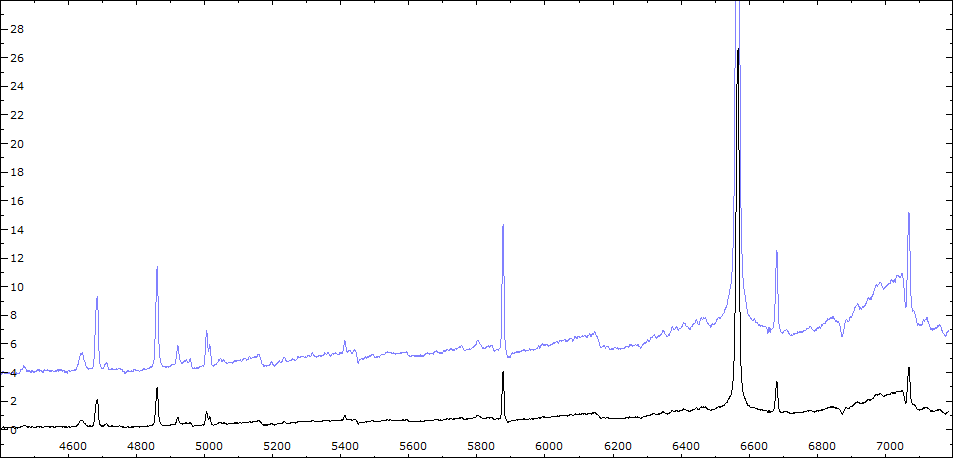
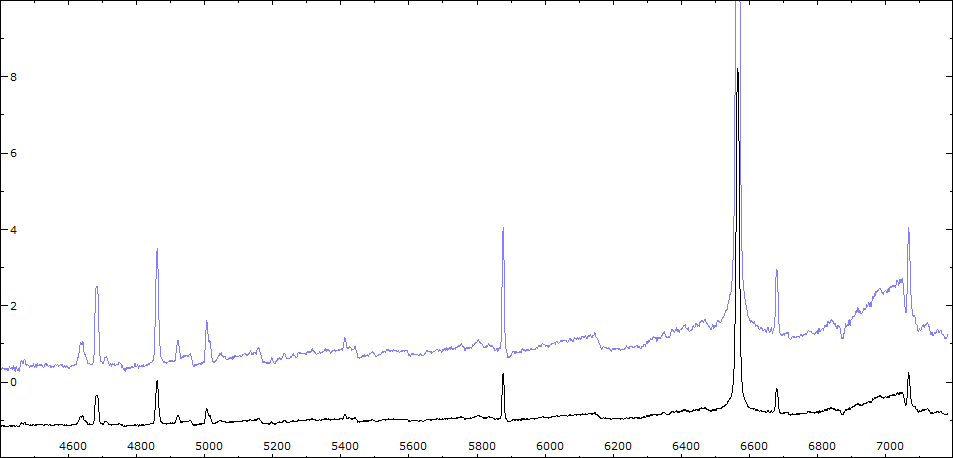
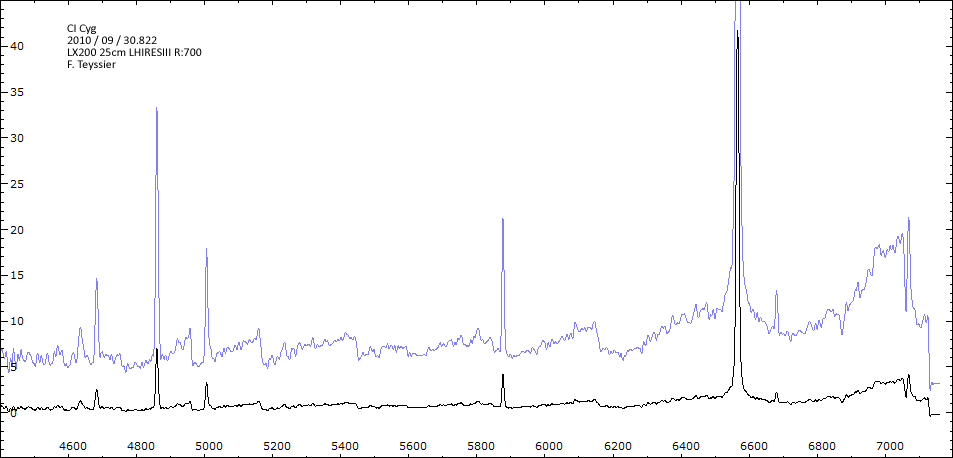
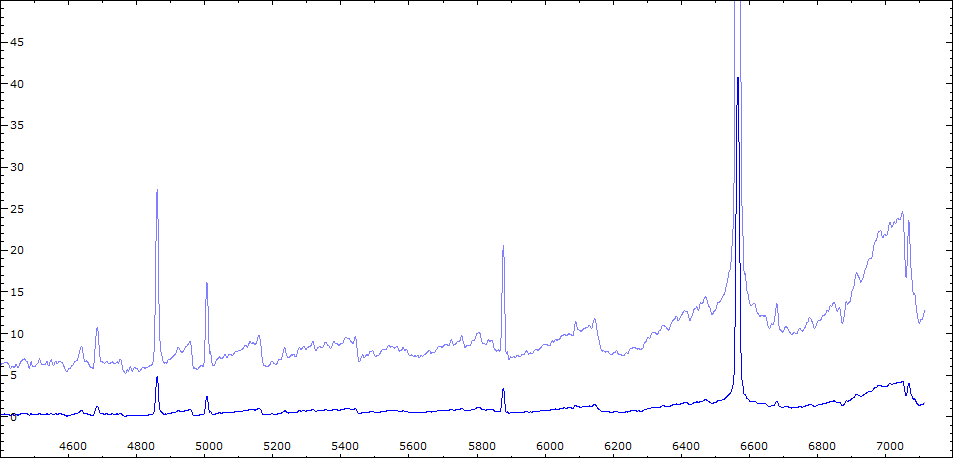
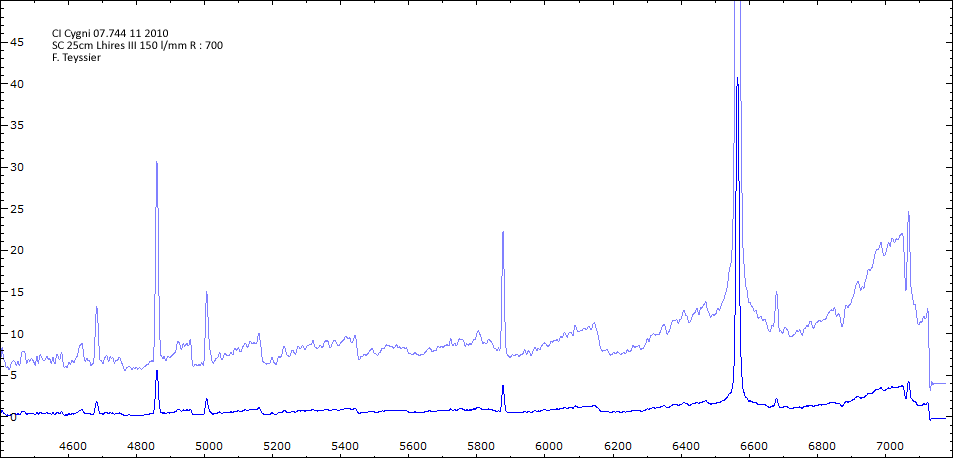
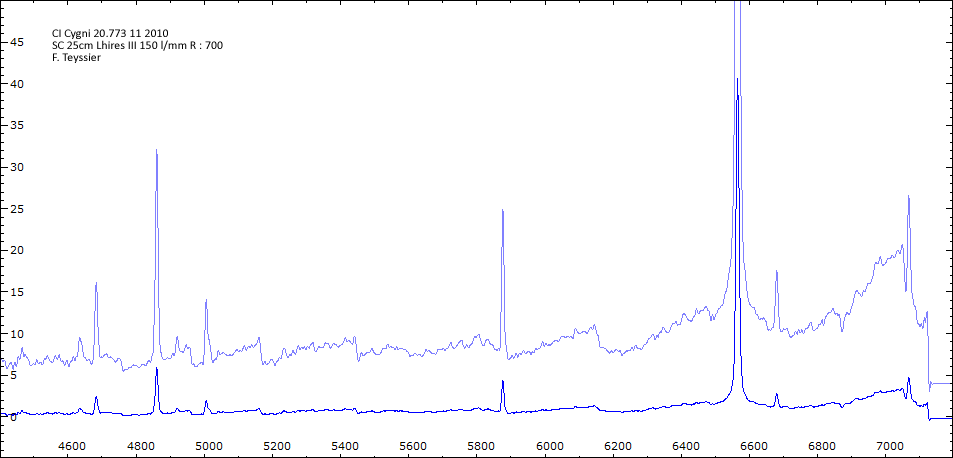
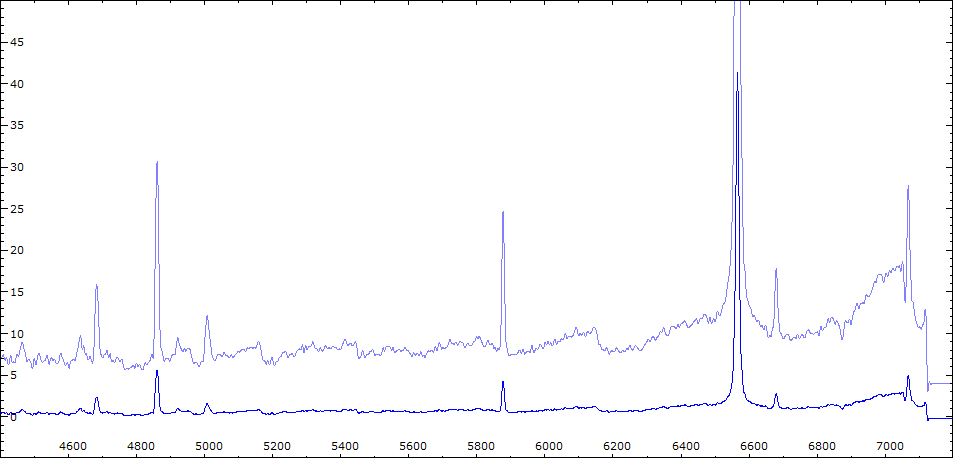
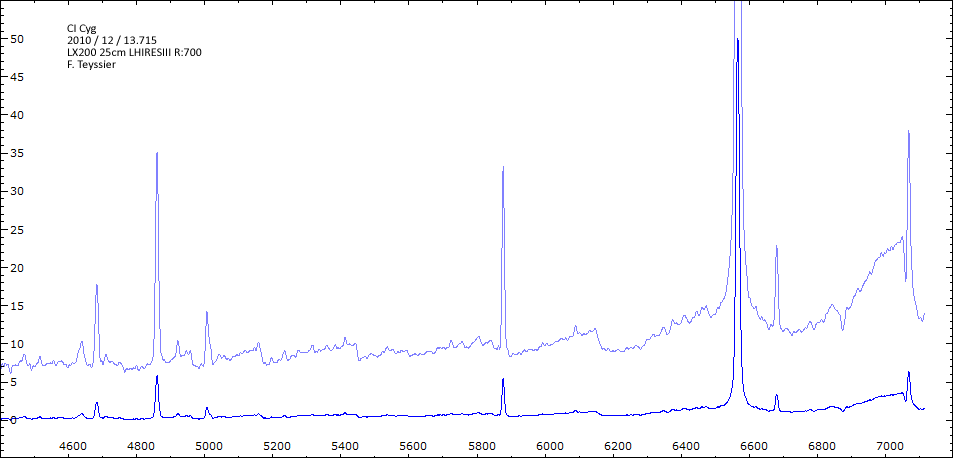
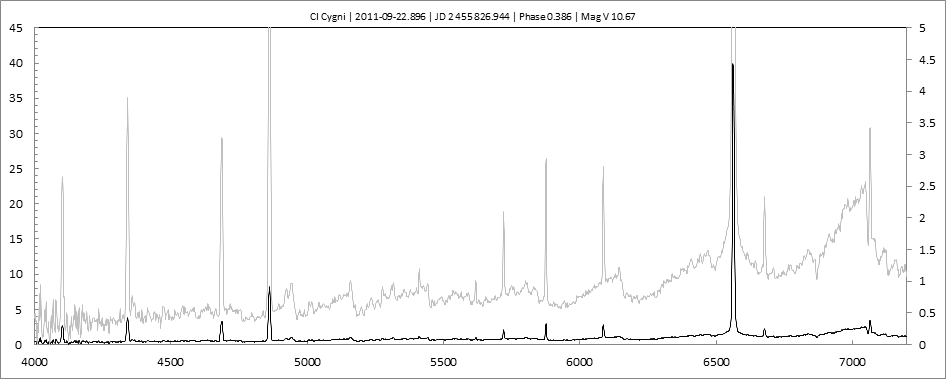
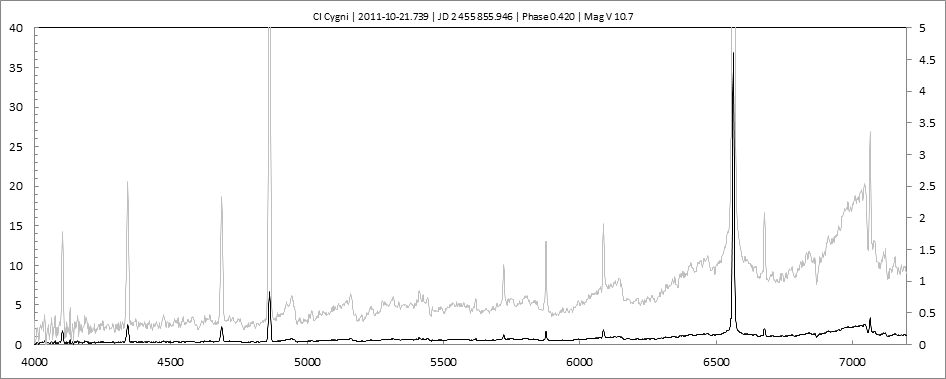
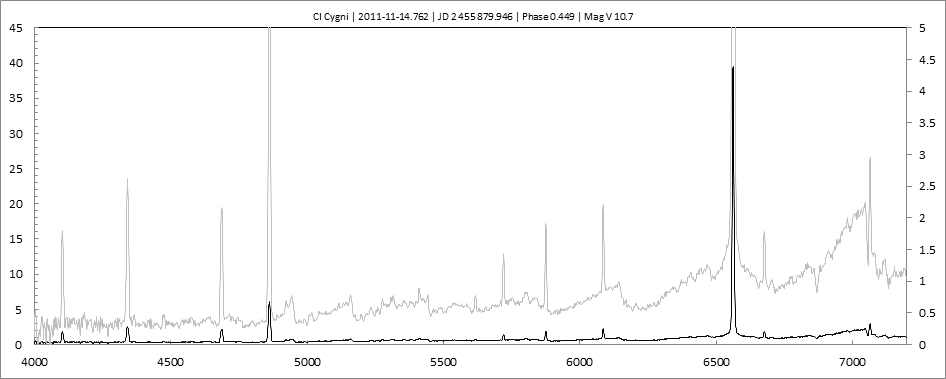
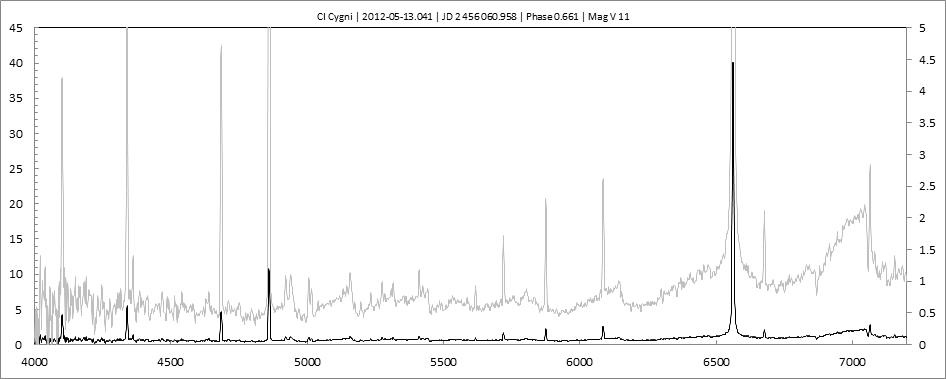
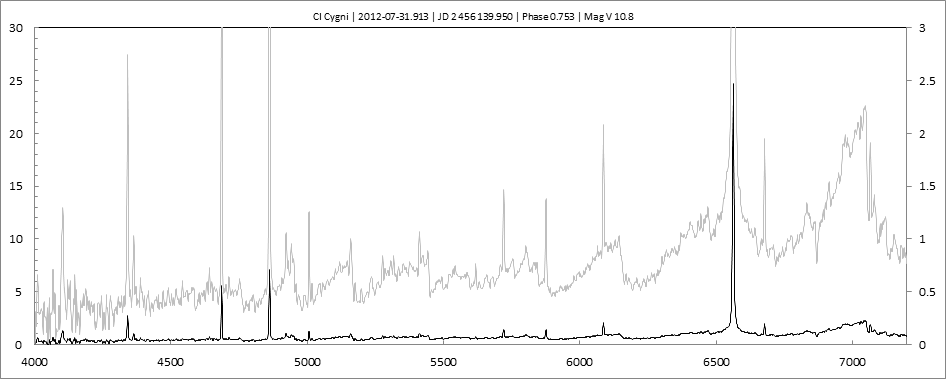
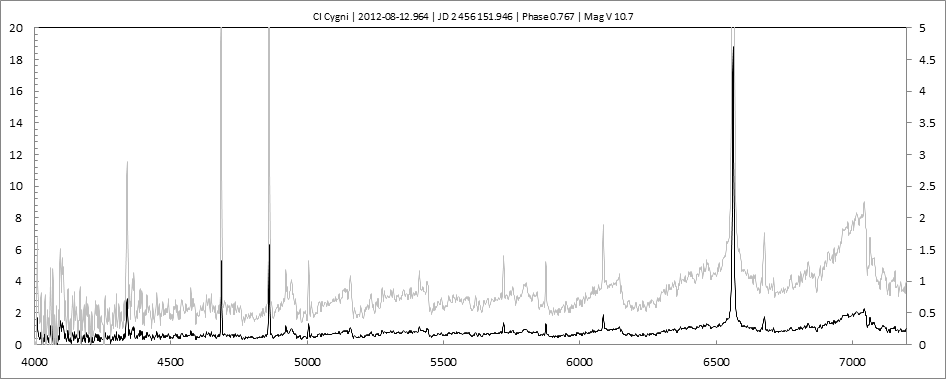
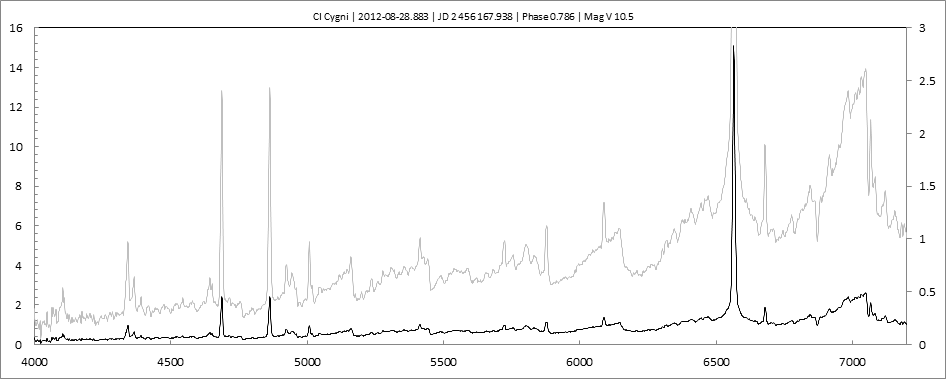
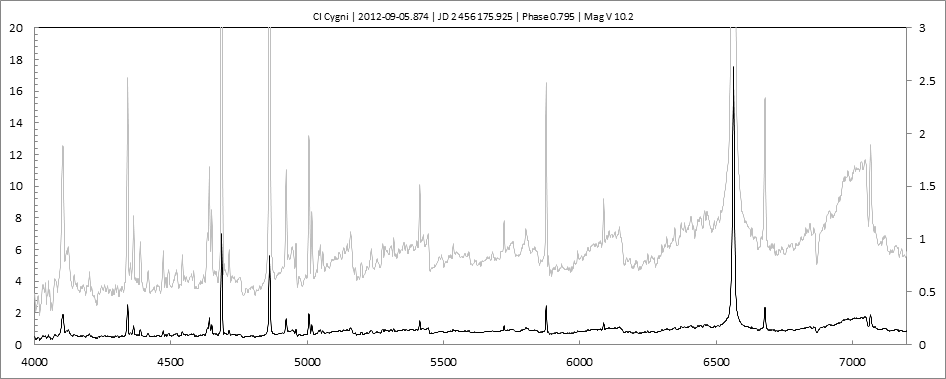
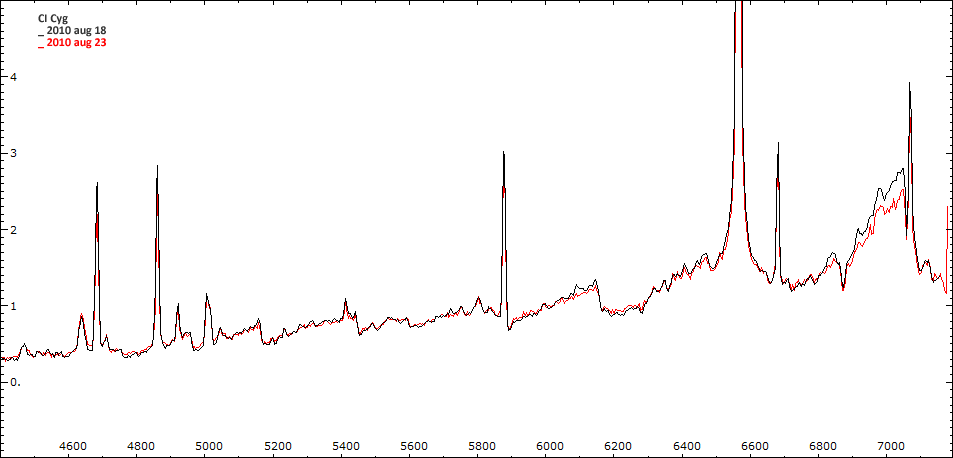
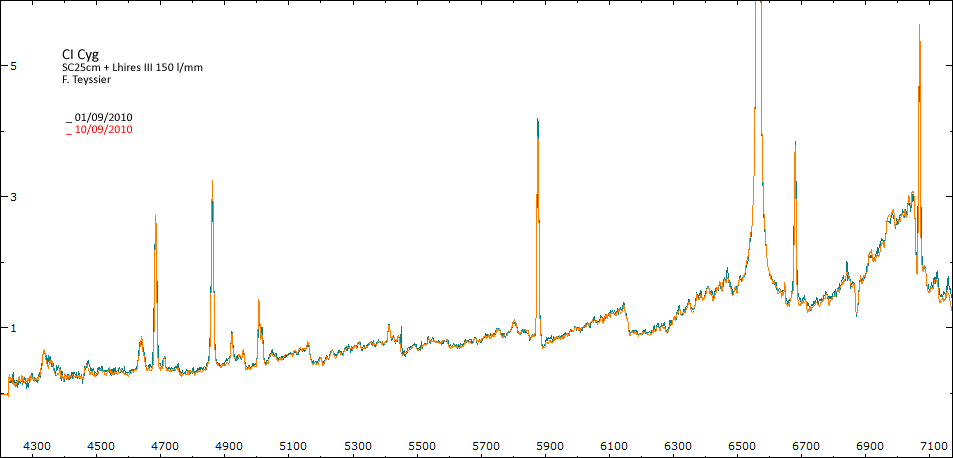
Les spectres basse résolution de l'outburst de 2010 sont présentés ci-dessous.
La page ARAS http://www.astrosurf.com/aras/CICyg/CI_Cyg.html regoupe plus de 70 spectres haute et basse résolution
Article CI Cygni : http://www.aavso.org/ejaavso143
Voir aussi : surveillance long terme de CI Cygni
Photométrie
Outbursts : 1911, 1937, 1971-73, 1975, 2008 et en cours
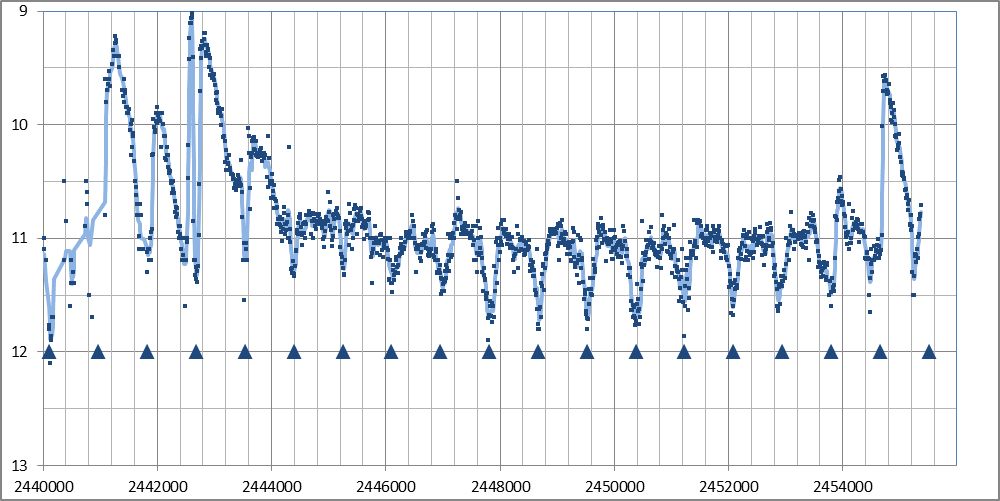
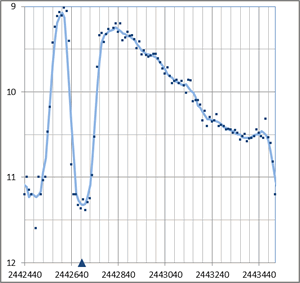
Courbe de luminosité (V+Vis) AAVSO. Les mesures sont moyennées par décades. Les triangles indiquent les minimas obtenus par l'éphéméride calculé par Mikolajewska, 1983.
On remarque la série d'outbursts de la période 1970-1978. Une éclipse intervient vers le maximum du 3ème outburst. Au plus profond de l'éclipse, la luminosité revient pratiquement au niveau atteint en phase quiescente : la zone produisant l'outburst est entièrement éclispée par la géante rouge du systéme.
Une nouvelle période d'outbursts s'est ouverte en 2008, avec un premier outburst culminant à mag 9.6 la première semaine d'octobre 2008. Le deuxième outburst a commencé sa progression (juin 2010). Il devrait atteindre son maximum dans les prochaines semaines. (voir ATEL #2732). La prochaine éclipse sera à sa profondeur maxi mi-novembre 2010.
Eclipse durant l'outburst de 1975
La durée de l'éclipse est d'environ 180 jours. La montée en luminosité dure 90 jours.
Ephéméride
Min = JD 2444396 + 855.25 E [Mikolajewska 1983]
Spectroscopie
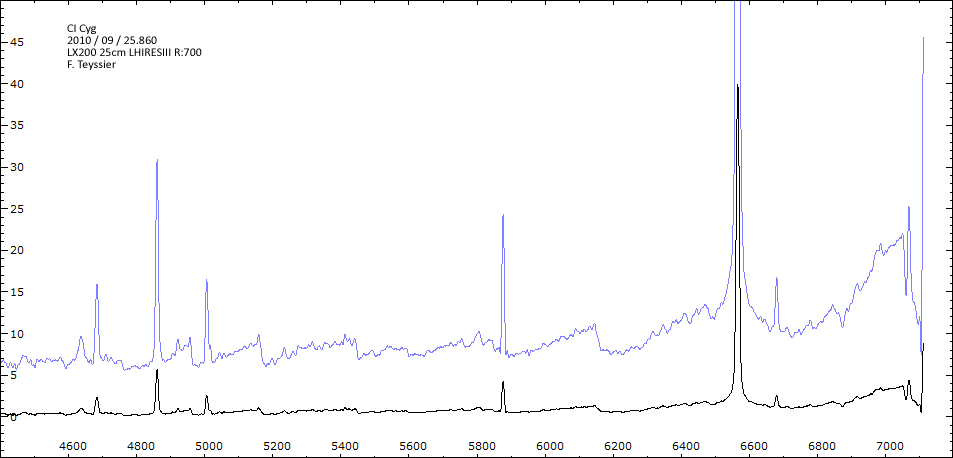
En état calme, le spectre de CI Cyg est celui d'une géante M5 sur lequel se superposent des raies intenses HI, HeI, HeII, [NV], [Fe VII]. [Fe X] a été détecté à certaines époques (Swing and Struve, 1940). [O III] est en général trés faible.
En outburst, le spectre change radicalement d'aspect pour prendre celui d'une géante F (F3 II/Ib). La naine blanche s'étend jusqu'à un rayon de 28 Rs (Siviero & al., 2009). Lors de la phase de montée en luminosité, Les raies de fortes excitation (He II, [Fe VII]) s'affaiblissent, de même que l'intensité des bandes TiO, alors que les raies [O III] et [Ne III] se renforcent.
Au maximum, He II et [FeVII], de même que [O III] et [Ne III] disparaissent. Les bandes TiO disparaissent dans le continuum de type F. Les raies HI sont trés brillantes, avec un profil P Cygni. Les raies d'absorption typiques des supergéantes F apparaissent.
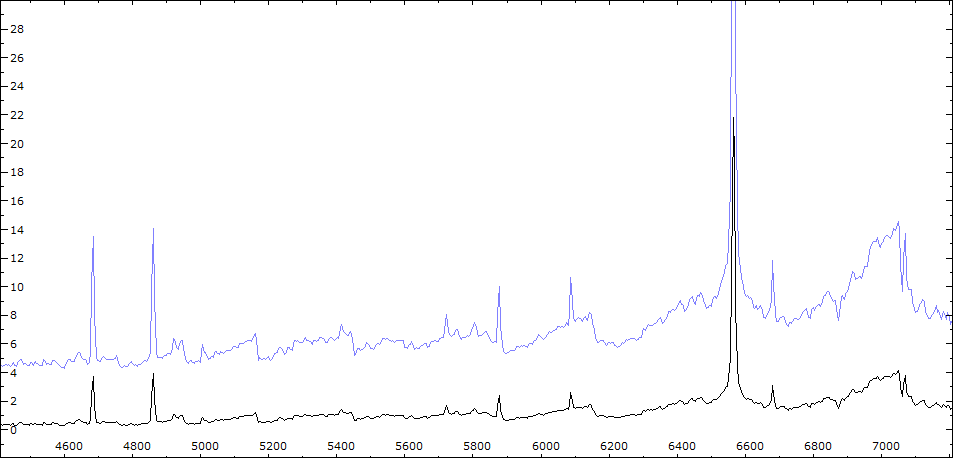
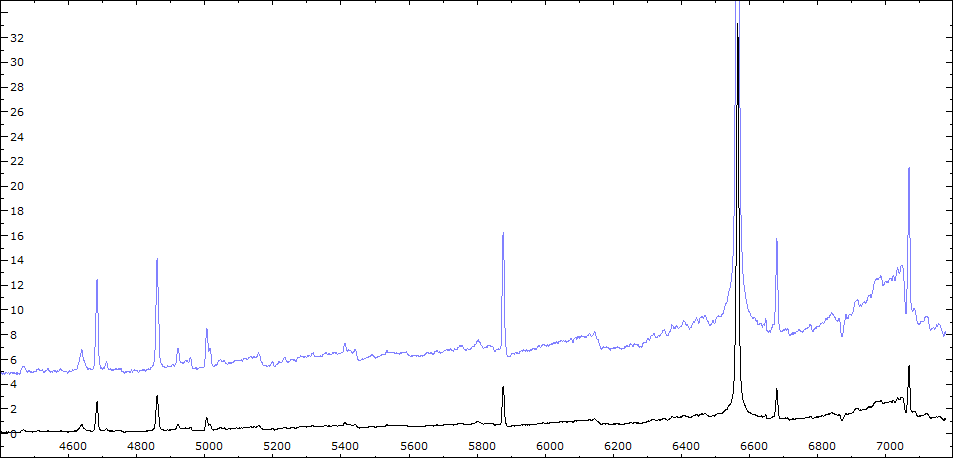
Identification des raies sur spectre du 30/06/2010
Suivi Outburst 2010
2010 Outburst monitoringCet outburst est le deuxième d'une nouvelle série. Il présente la particularité de coïncider avec une éclipse.
Courbe luminosité CCD V (AAVSO) Comparaison des éclipses de 1975 (Rouge) et 2010 (Bleu)
SC 25cm LHIRES III 150 t/mm R : 700 Starlight SXV-H9
Magnitudes from AAVSO database
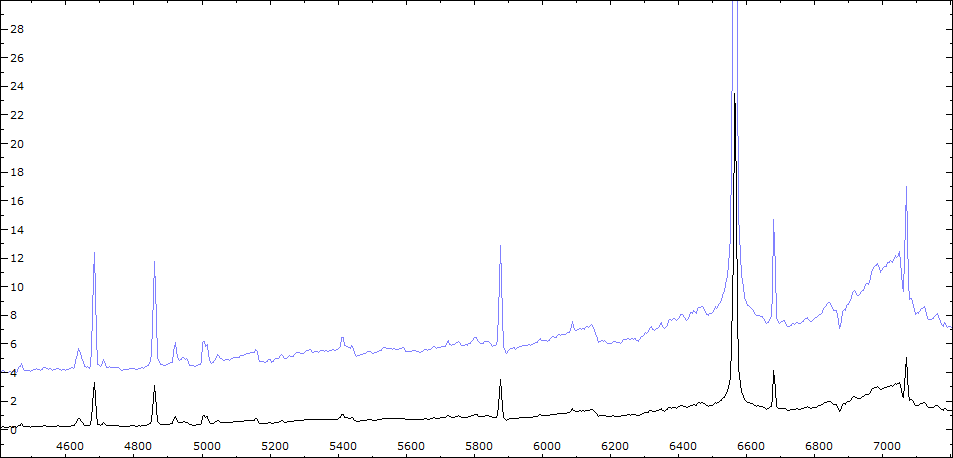
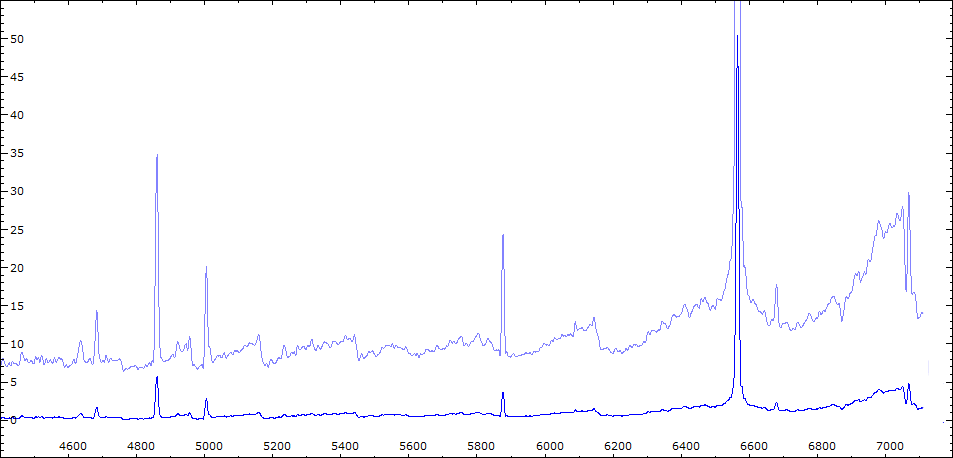
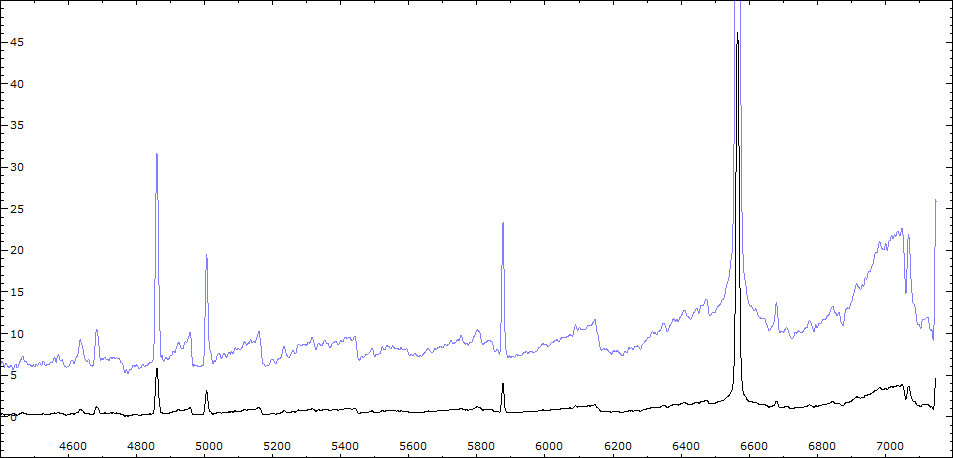
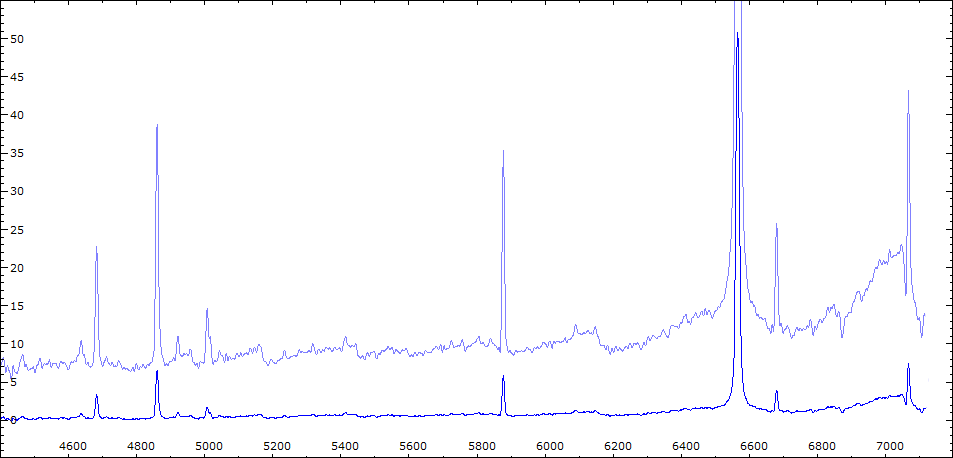
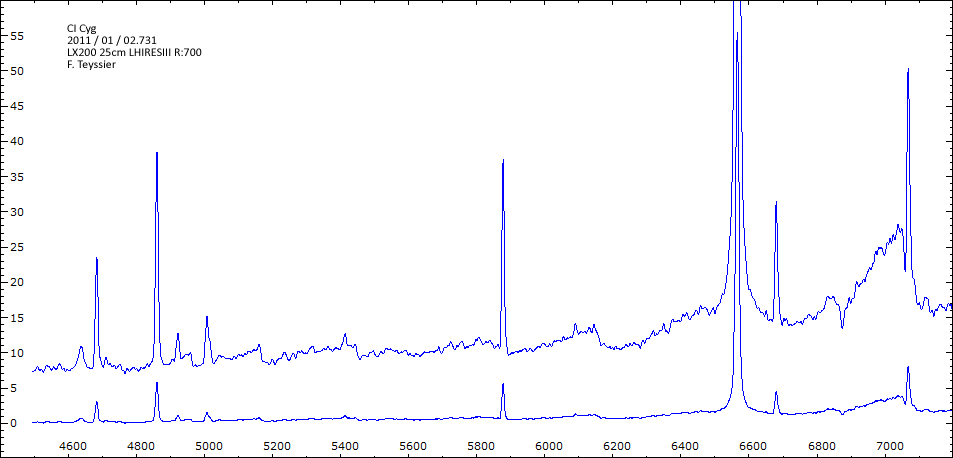
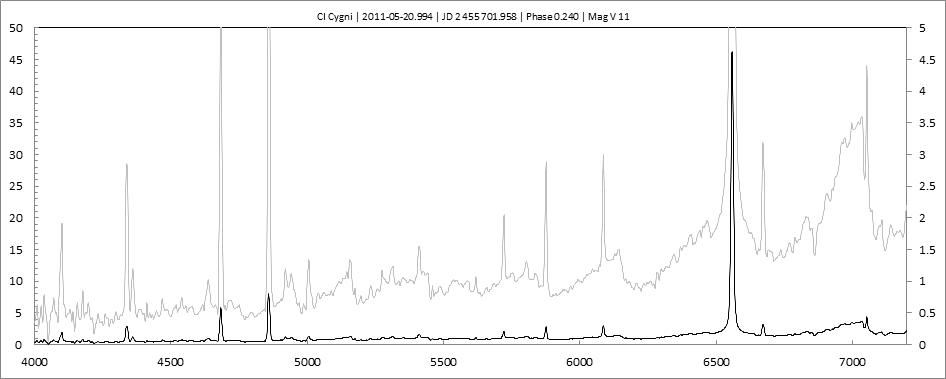
Date 30 06 2010 Heure TU 22:00 Exp 6 x 600 sec Phase -0.135
Mag V 11.0
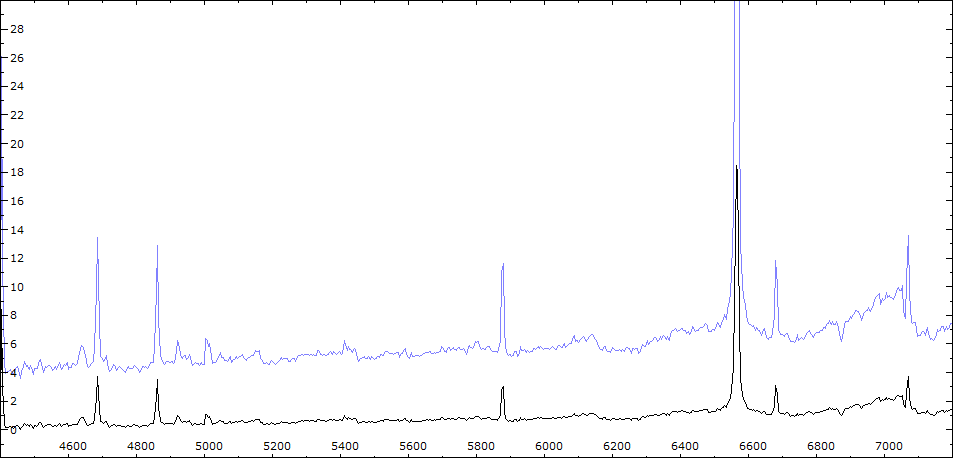
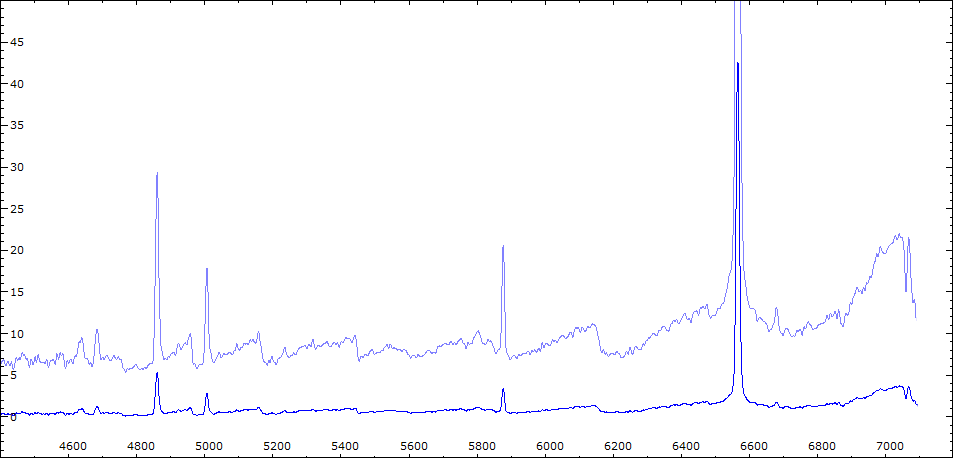
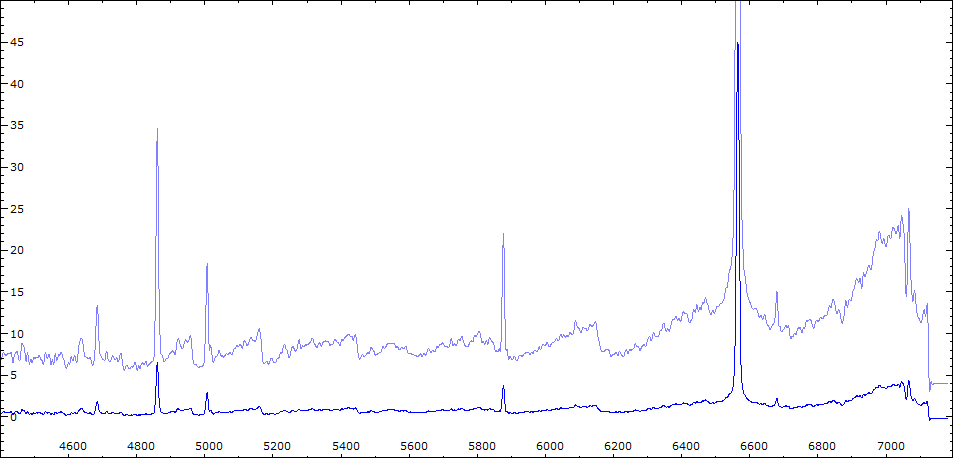
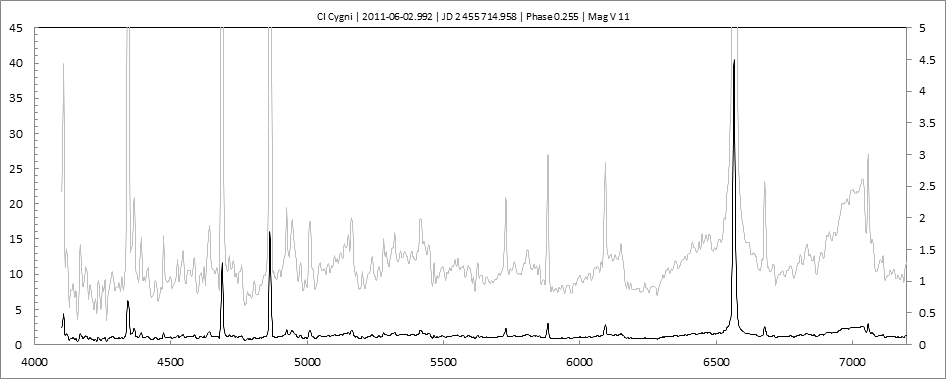
Date 24 07 2010 Heure TU 21:26 Exp 6 x 600 sec Phase -0.107 Mag V 10.6
Date 02 08 2010 Heure TU 21:40 Exp 6 x 600 sec Phase -0.097 Mag V 10.2
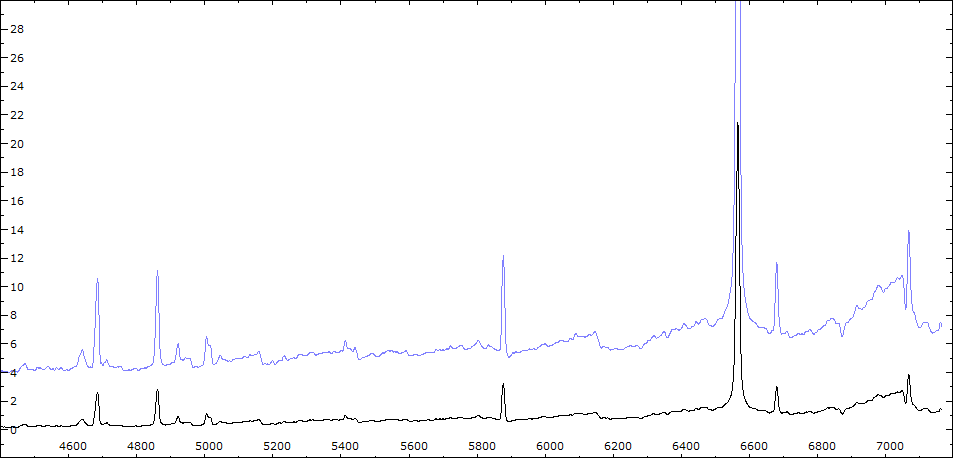
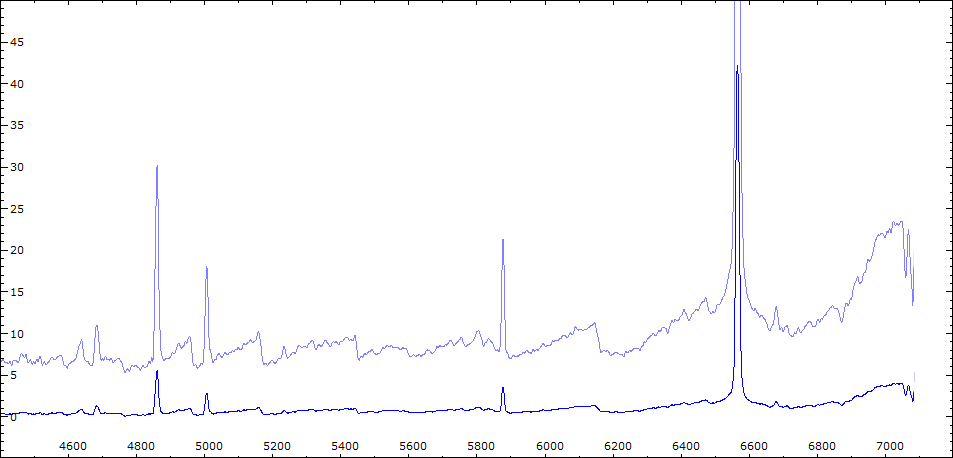
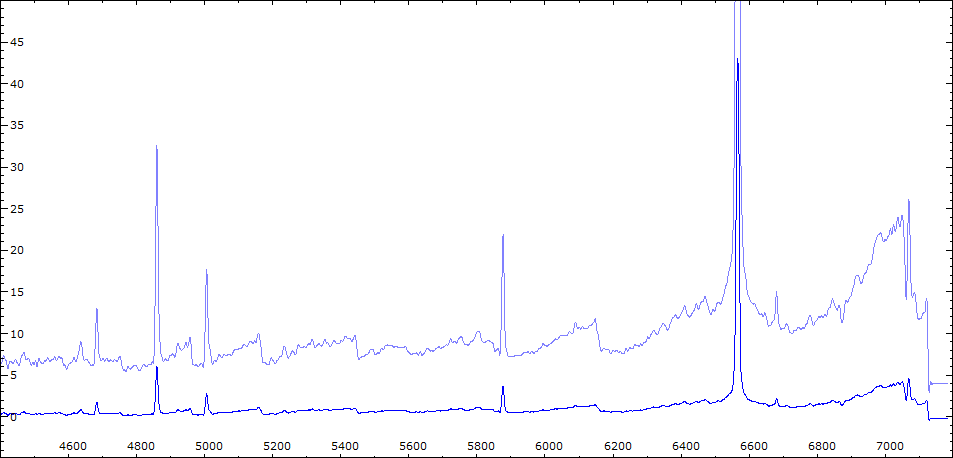
Date 09 08 2010 Heure TU Exp 8 x 300 sec Phase -0.090 Mag V 10,2
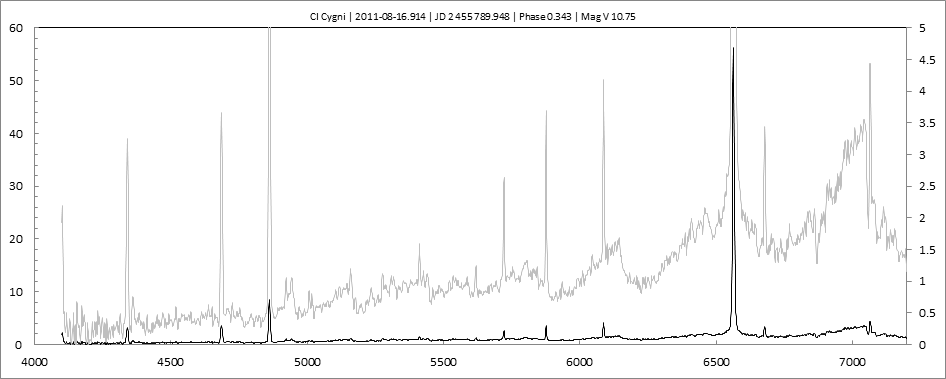
Date 18 08 2010 Heure TU 21:22 Exp 8 x 300 sec Phase -0.078 Mag V 10.6
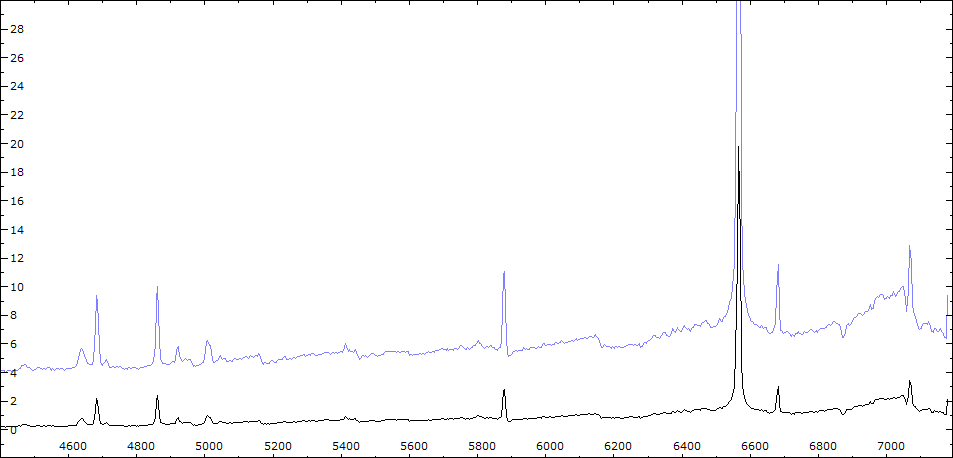
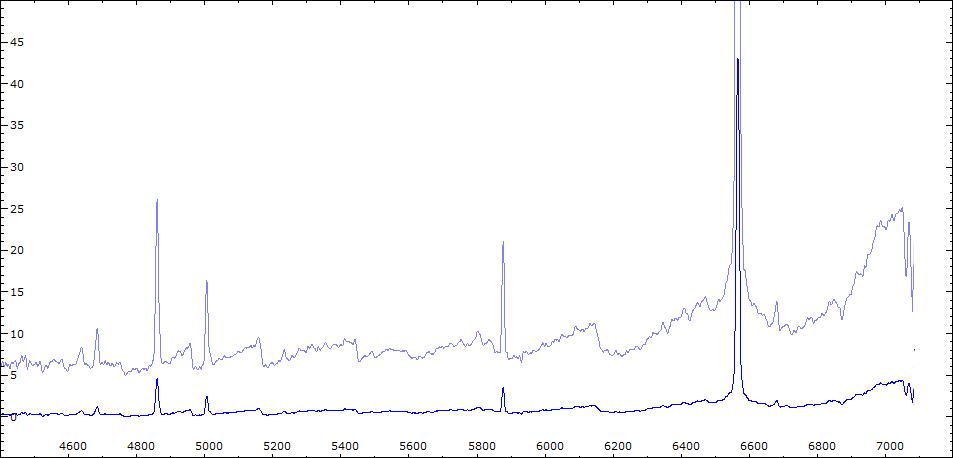
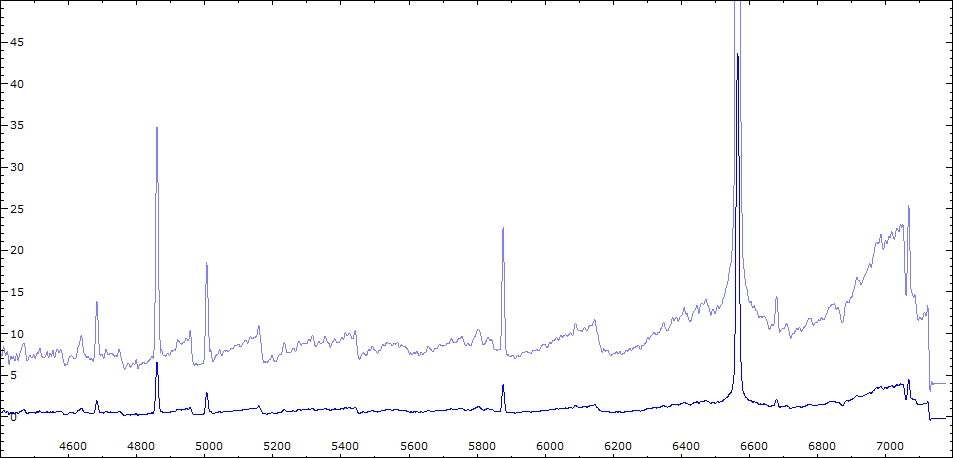
Date 23 08 2010 Heure TU Exp 5 x 300 s Phase -0.072 Mag V 9.8
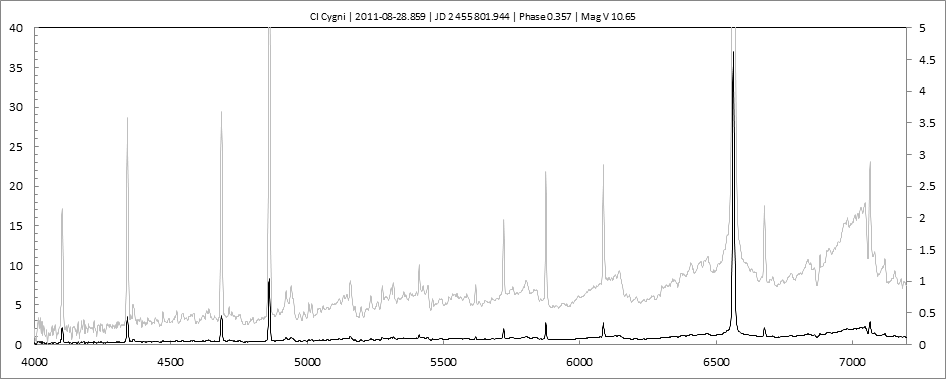
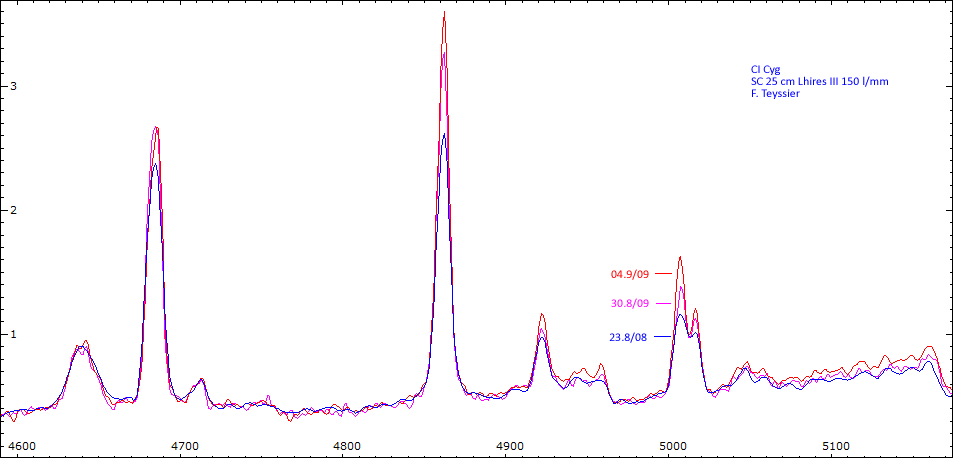
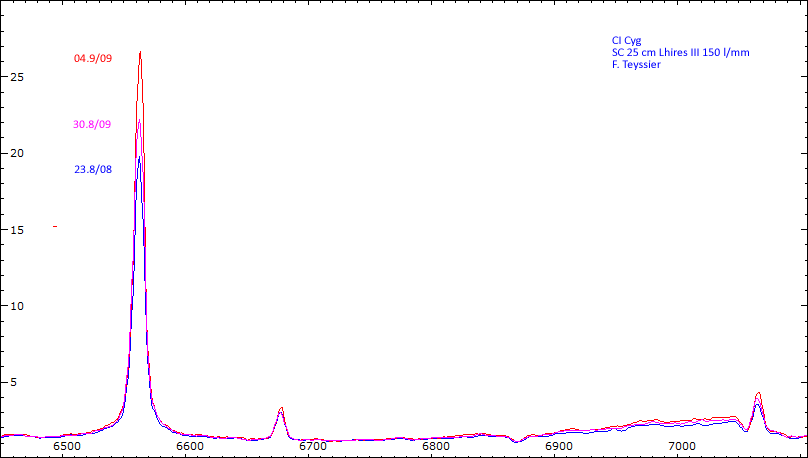
Date 30 08 2010 Heure TU Exp 9 x 300 s Phase -0.064 Mag V 9.95
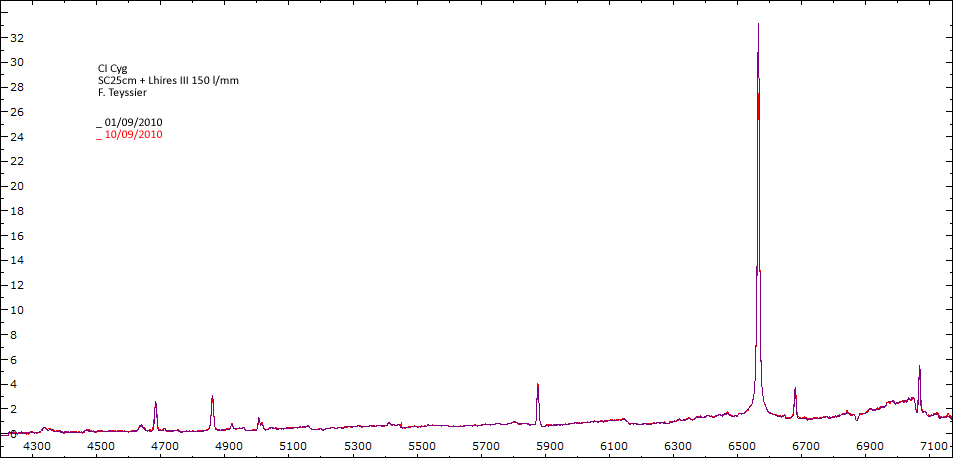
Date 01 09 2010 Heure TU Exp 9 x 300 s Phase -0.062 Mag V 9.8
Date 04 09 2010 Heure TU Exp 4 x 600 s Phase -0.058 Mag V 10.12
Date 08 09 2010 Heure TU Exp 5 x 600 s Phase -0.054 Mag V 10.2
Date 10 09 2010 Heure TU 20:02 Exp 4 x 600 s Phase -0.051 Mag V 10.2
Date 17 09 2010 Heure TU 21:12 Exp 6 x 600 s Phase -0.043 Mag V 10.4
Date 22 09 2010 Heure TU 21.20 Exp 8 x 300 s Phase -0.037 Mag V 10.6
Date 25 09 2010 Heure TU 21:39 Exp 8 x 300 s Phase -0.034 Mag V 10.8
Date 30.09 2010 Heure TU 19:44 Exp 5 x 300 s Phase -0.028 Mag V 10.6
Date 07 10 2010 Heure TU 19:48 Exp 11 x 300 s Phase -0.020 Mag V 11.1
Date 09 10 2010 Heure TU 19:36 Exp 12 x 300 s Phase -0.017 Mag V 11.13
Date 12 10 2010 Heure TU 19:48 Exp 8 x 300 s Phase -0.014 Mag V 11.14
Date 16 10 2010 Heure TU 19:35 Exp 12 x 300 s Phase -0.009 Mag V 11.15
Date 17 10 2010 Heure TU 19:14 Exp 16 x 300 s Phase -0.008 Mag V 11.14
Date 20 10 2010 Heure TU 19:25 Exp 13 x 300 s Phase -0.004 Mag V 11.13
Date 22 10 2010 Heure TU 18:40 Exp 15 x 300 s Phase -0.002 Mag V 11.1
Date 25 10 2010 Heure TU 19:36 Exp 12 x 300 s Phase 0.001 Mag V 11.1
Date 30 10 2010 Heure TU 18:59 Exp 8 x 300 s Phase 0.007 Mag V 10.96
Date 31 10 2010 Heure TU 18:51 Exp 10 x 300 s Phase 0.009 Mag V 10.95
Date 01 11 2010 Heure TU 18:36 Exp 8 x 300 s Phase 0.010 Mag V 10.94
Date 07 11 2010 Heure TU 17:51 Exp 8 x 300 s Phase 0.017 Mag V 10.8
Date 20 11 2010 Heure TU 17:51 Exp 8 x 300 s Phase 0.032 Mag V 10.65
Date 03 12 2010 Heure TU 18:51 Exp 16 x 300 s Phase 0.048 Mag V 10.6
Date 13 12 2010 Heure TU 17 : 10 Exp 12 x 200 Phase 0.058 Mag V 10.6
Date 25 12 2010 Heure TU 18 : 58 Exp 7 x 300 s Phase 0.072 Mag V 10.6
Date 02 01 2011 Heure TU 17:32 Exp 7 x 300 s Phase 0.081 Mag V 10.6 __ Observations 2011 _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__ Observations 2012 _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Outbust 2010
Evolution
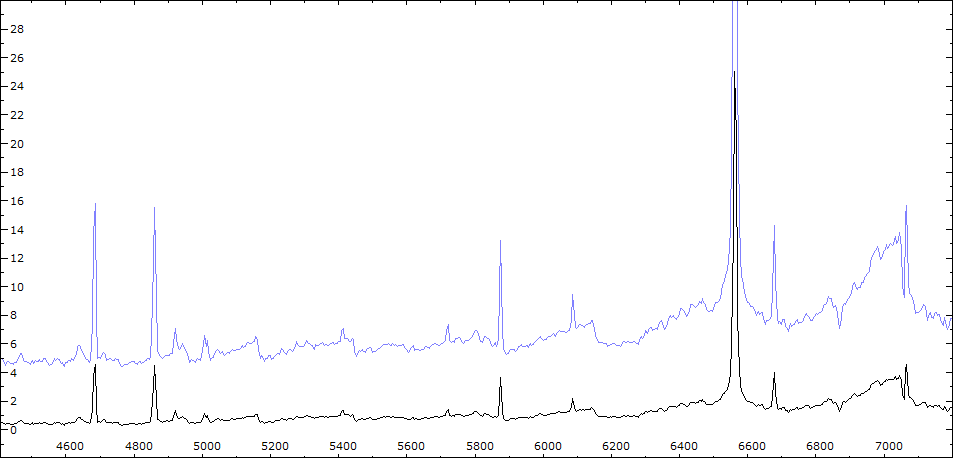
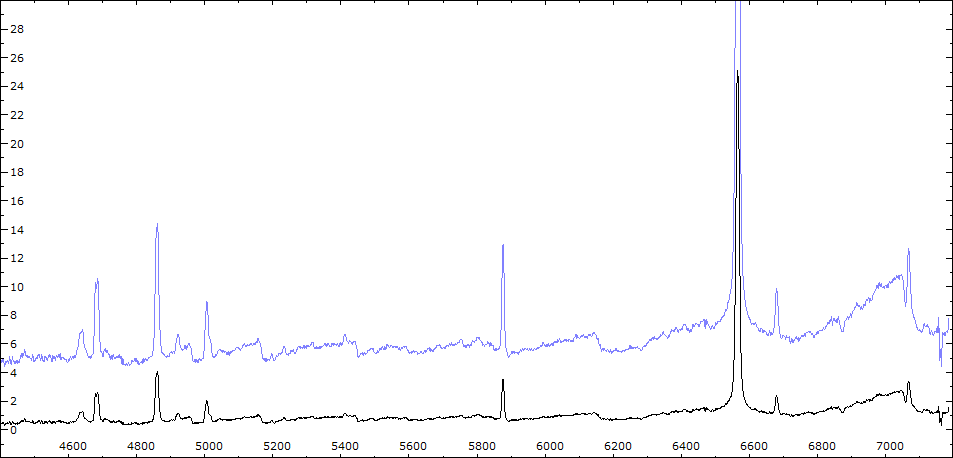
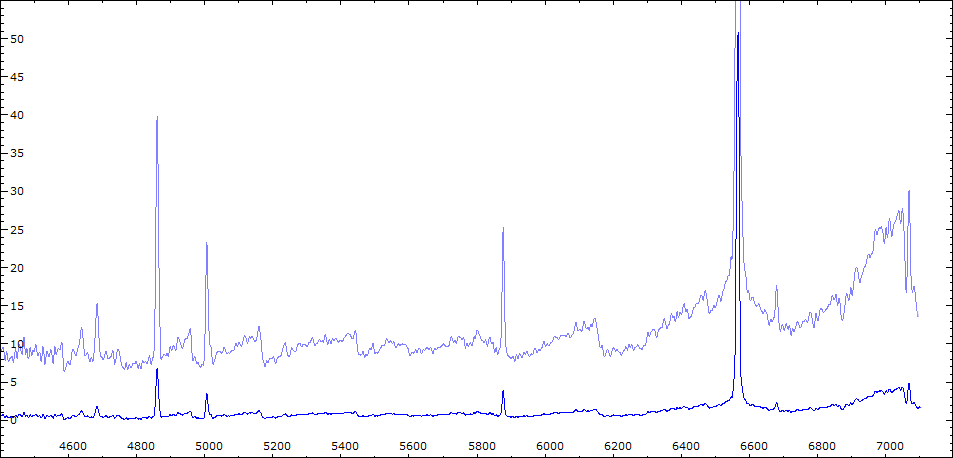
Comparaison spectres du 30/06 (noir) et 02/08/2010 (rouge)
On note : affaiblissement des bandes TiO - augmentation de l'intensité HeI - effondrement des raies interdites de forte ionisation
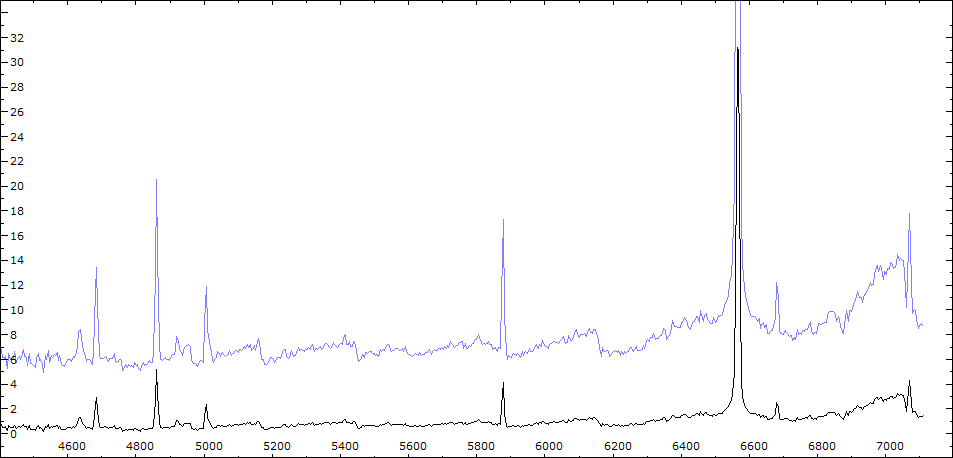
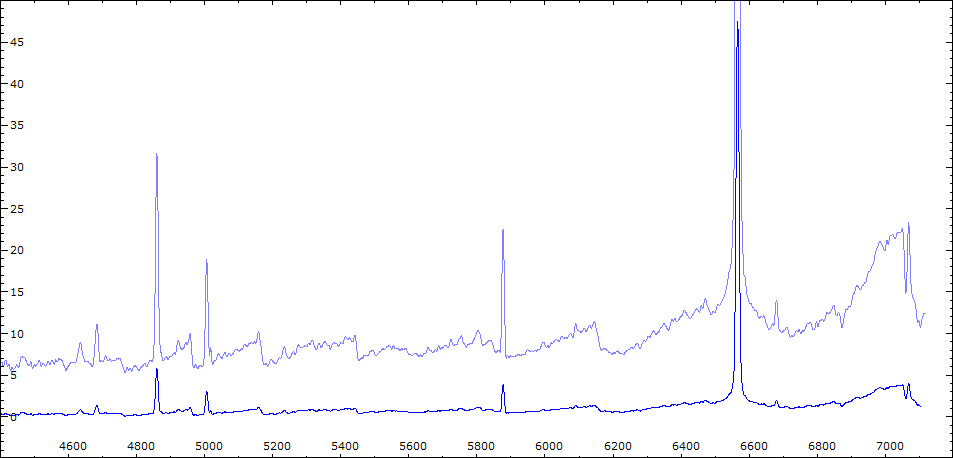
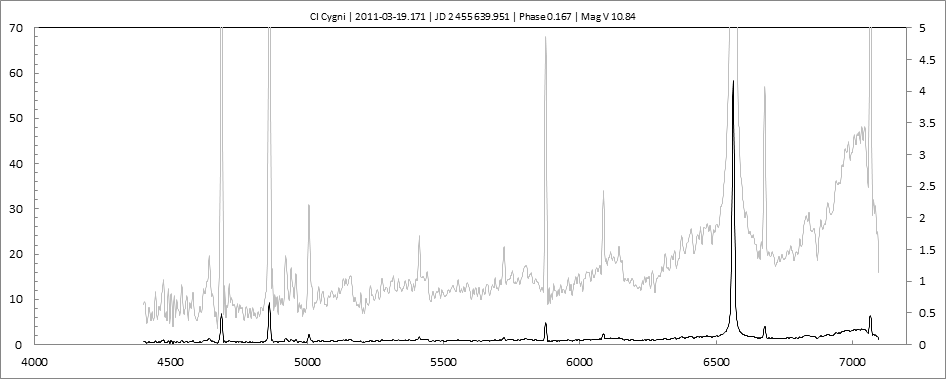
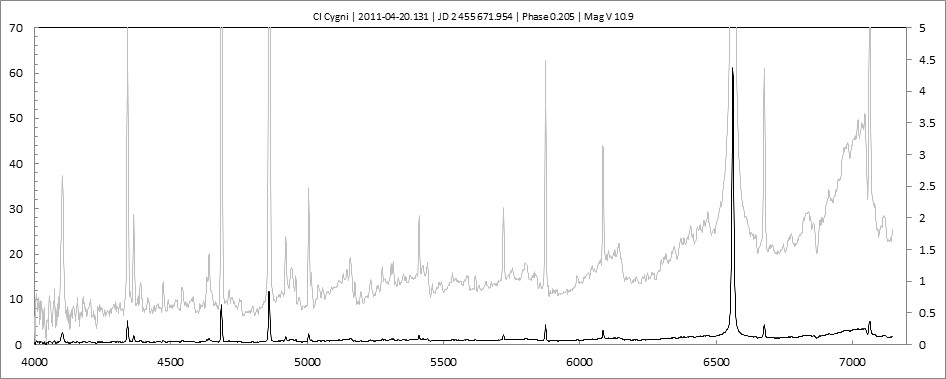
Début de l'éclipse
Début mars 2011, les raies de forte excitation ont considérablement augmenté par rapport au spectre de novembre 2010 (sortie éclipse et fin outburst).
L'intensité de [FeVII] a retrouvé le niveau du début de l'outburst (spectre de juin 2010). HeI, HeII et HI sont nettement plus intenses.
On notera également la largeur de H alpha sensiblement plus importante qu'en juin 2010.
Equivalent widths (in angtröms) during 2010 outburst
H alpha H alpha (relative to Hb = 100) H béta He I 5876 He II EW [OIII]/ EW He I 5016
Ajustement gaussien sur spectre Thierry Garrel (26/10/2010)
Cette méthode permet de déterminer les paramètres des différents composants de la raie Ha. Dans l'exemple ci dessus, 6 composants ont été utilisés afin d'ajuster au mieux
Voir aussi : http://www.astrosurf.com/aras/CICyg/CI_Cyg.html
Publications
CI Cygni: the eclipse of the hot component, which is in strong outburst, is entering the phase of totality
ATel #2913; U. Munari (INAF Padova-Asiago), P. Valisa, A. Milani, G. Cherini, F. Castellani, S. Dallaporta, A. Siviero, A. Frigo (ANS Collaboration)
on 9 Oct 2010; 18:46 UT
Subjects: Optical, Binaries, Cataclysmic Variables, Novae
The symbiotic star CI Cyg is undergoing a major outburst phase that begun in 2008 (Munari et al. 2008, CBET #1487, Siviero et al. 2009, MNRAS 399, 2139), the first one after 30 years of flat quiescence. The current outburst phase is a close copy of the multi-maxima eruption that CI Cyg experienced in 1970-78. After a maximum at B=10.28, V=9.50, V−Rc=+0.80, V−Ic=+2.07 that occurred on the first week of October 2008, the star started to decline, reaching a minimum brightness B=12.1, V=11.0, V−Ic=+3.2 during March, 2010, values which are not too far away from to those observed during the long preceding quiescence. Almost immediately after, the star bounced back and started a rapid rise toward a second maximum (Munari et al. 2010, ATel #2732).
The rise toward a second maximum proceeded fast and unperturbed until August 24, 2010 when the star was measured at B=10.67 V=9.73, V−Rc=+1.14, V−Ic=+2.36. At that time, an eclipse of the outbursting component, by the M6III cool giant companion, started to become noticeable. The decline in magnitude has been linear since then. On 8 October 2010 the system has weakened to B=12.4, V=11.1, V−Rc=+1.40, V−Ic=+3.22, which are the same as at the center of totality during the last eclipse, which occurred in 2008. The orbital period of CI Cyg is 853.8 days.
The current eclipse, and in particular the totality phase that is starting right now, offer relevant opportunities to study the outer regions of the ionized circumstellar medium and to derive absolute magnitude, radius and temperature of the component in outburst.
The eclipse is deeply affecting the spectral appearance too. Comparing our Echelle spectra for August 21 (immediately before the beginning of the eclipse) and October 5, at the bottom of the eclipse, now the veiling of the absorption spectrum of the M6III giant is greatly reduced, and the relative intensity of emission lines largely different. The ratio of HeII/Hbeta equivalent widths changed from 1.58 on August 21 to 0.30 on October 5, for [OIII] 5007/HeI 5016 from 1.37 to 10.4, for OI 8446/Paschen from 2.4 to 15, for Halpha/HeI 6678 from 12 to 46, for [FeVII] 6087/[OI] 6300 from 2.5 to 1.5, and for Hgamma/[OIII] 4363 from 1.23 to 1.45. The sharp absorption component superimposed on Balmer and Paschen emission lines has reduced in strength, and the [OIII] lines changed from a saddle profile with a velocity separation of 70 km/sec to a more Gaussian one with FWHM=140 km/sec.
ATEL #2732
Title: CI Cyg toward a new maximum in current major outburst phase
Author: U. Munari, A. Siviero (INAF Padova-Asiago), G. Cherini, S.
Dallaporta, P. Valisa (ANS Collaboration)
Queries: ulisse.munari@oapd.inaf.it
Posted: 12 Jul 2010; 15:16 UT
Subjects: Cataclysmic Variables, Novae, VariablesThe symbiotic star CI Cyg is on a steep rise toward a second maximum in
the major outburst phase it entered in 2008 (Munari et al. 2008, CBET
1487), the first one after 30 years of flat quiescence.CI Cyg has experienced only a few outbursts in its long recorded
history. The outbursts of 1911 and 1937 have been modest in both brightness
amplitude and duration. Then, between 1970 and 1978 CI Cyg experienced
a major outburst phase, characterized by three maxima occurring on Nov
1971 (V=9.3), Nov 1973 (V=9.8) and Aug 1975 (V=8.7) and minima (V=11.1)
on Jun 1973 and Mar 1975. One further and sharper minimum, centered
on Oct 4, 1975 (at V=11.1), was caused by a total eclipse of the outbursting
component by the M5.5 III companion, following the ephemeris Min(V)
= 2442690 + 853.8xE (Belyakina 1984, Izv.Krym.Astrofiz.Obs. 68, 108;
Fekel et al. 2000, AJ 119, 1375).The current outburst is a close copy of that CI Cyg experienced in
1970-78. After a maximum at V=9.50, B−V=+0.78, V−Rc=+0.80,
V−Ic=+2.07 that occurred on the first week of October 2008 (Siviero
et al. 2009, MNRAS 399, 2139), CI Cyg declined steadily and reached
minimum brightness at V=11.0, B-V=+1.1, V−Ic=+3.2 on March 2010.
The time delay between maximum and minimum has been about about 550
days, as for the 1970-78 event. At the time of the latter, a rise
toward a second maximum started soon after the first minimum. The same
is occurring right now, with CI Cyg currently on the rise toward a new
maximum. The last measurement we collected gives V=10.44, B-V=+1.19,
V-Rc=+1.18, V-Ic=+2.88 on July 9, 2010.If the similarity with the 1970-78 active phase will be maintained,
the second maximum around V=9.8 should be reached in a few weeks time.2009MNRAS.399.2139S
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 399, 2139-2145 (2009)
The ongoing 2008-09 outburst of CI Cyg.
SIVIERO A., MUNARI U., DALLAPORTA S., VALISA P., LUPPI V., MORETTI S., TOMASELLI S., BACCI S., BALLARDINI F., CHERINI G., GRAZIANI M., FRIGO A. and VAGNOZZI A.1991AJ....101..637K
Astron. J., 101, 637-654 (1991)
On the nature of the symbiotic binary CI Cygni.
KENYON S.J., OLIVERSEN N.A., MIKOLAJEWSKA J., MIKOLAJEWSKI M., STENCEL R.E., GARCIA M.R. and ANDERSON C.M.1985AcA....35...65M
Acta Astron., 35, 65-95 (1985)
On the nature of CI Cygni.
MIKOLAJEWSKA J.1985IBVS.2834....1G
IAU Inform. Bull. Var. Stars, 2834, 1-4 (1985)
Photometry and spectrophotometry of symbiotic stars : CI Cyg, Z And, V1016 Cyg, HM Sge, HBV 475.
GRAVINA R.1983AcA....33..403M
Acta Astron., 33, 403-429 (1983)
A spectrophotometric study of CI Cygni during the 1980 eclipse.
MIKOLAJEWSKA J. and MIKOLAJEWSKI M.1983ApJ...268..250O
Astrophys. J., 268, 250-263 (1983)
Observational studies of the symbiotic stars. II. Emission-line relative intensity variations in CI Cygni, BF Cygni, AX Persei, and V1016 Cygni.
OLIVERSEN N.A. and ANDERSON C.M.1983IBVS.2355....1M
IAU Inform. Bull. Var. Stars, 2355, 1-4 (1983)
Emission line intensity varations during the 1982 eclipse of CI Cygni.
MIKOLAJEWSKA J.1981A&A....94..290I
Astron. Astrophys., 94, 290-293 (1981)
Spectrophotometric observations of CI Cyg in 1979.
IIJIMA T.1981A&AS...46..257F
Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser., 46, 257-261 (1981)
Observations spectroscopiques de CI Cygni.
FEHRENBACH C. and CHUN H.C.1981IBVS.1945....1G
IAU Inform. Bull. Var. Stars, 1945, 1-2 (1981)
Spectroscopic observations of CI Cyg in 1980.
GRAVINA R.1981IBVS.2041....1G
IAU Inform. Bull. Var. Stars, 2041, 1-4 (1981)
Spectroscopic observations of symbiotic stars in July and September 1981.
GRAVINA R.1980IBVS.1759....1G
IAU Inform. Bull. Var. Stars, 1759, 1-2 (1980)
Spectroscopic observations of CI Cygni in 1978 and 1979.
GRAVINA R.1954AnAp...17....6T
Ann. Astrophys., 17, 6 (1954)
Les spectres de BF Cygni, AX Persei et CI Cygni en 1952.
TCHENG M.L. and BLOCH M.1953AnAp...16...73B
Ann. Astrophys., 16, 73 (1953)
Spectrophotometrie de T CrB de 1946 a 1952.
BLOCH M. and TCHENG M.L.1953PDAO....9..321A
Publ. Dominion Astrophys. Obs., 9, 321 (1953)
Spectrographic studies of the combination variables Z Andromedae, BF Cygni, CI Cygni.
ALLER L.H.1953PDAO....9..321A
Publ. Dominion Astrophys. Obs., 9, 321 (1953)
Spectrographic studies of the combination variables Z Andromedae, BF Cygni, CI Cygni.
ALLER L.H.