Projets Spectroscopie 1
Etoiles Symbiotiques
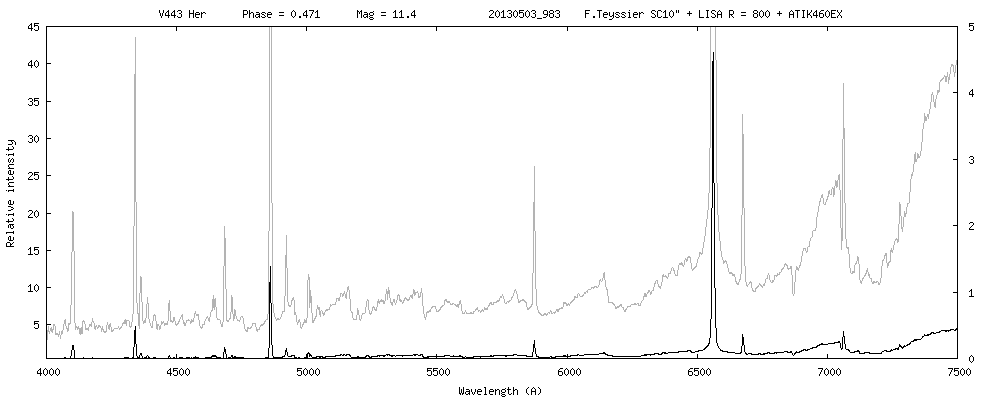
V443 Her
![]()
AD [2000] DE [2000] Mag Type P Orb [j] Spec E(B-V)
History Light Curve Spectroscopy
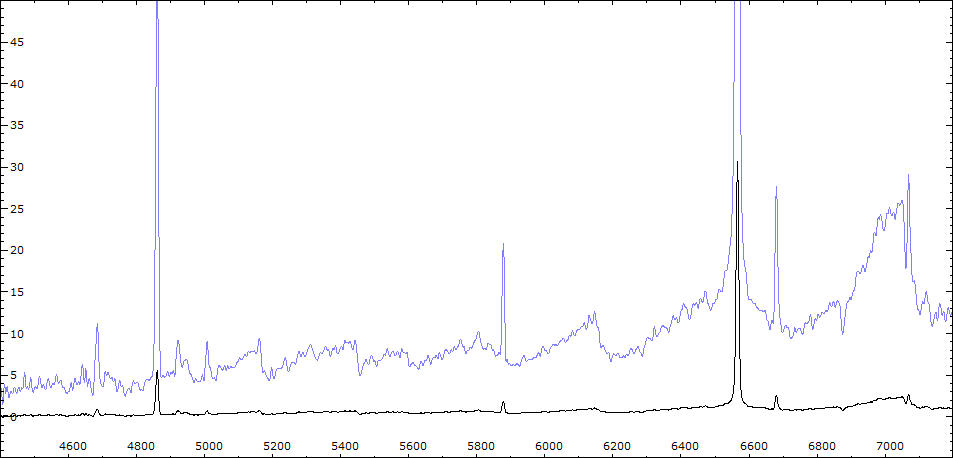
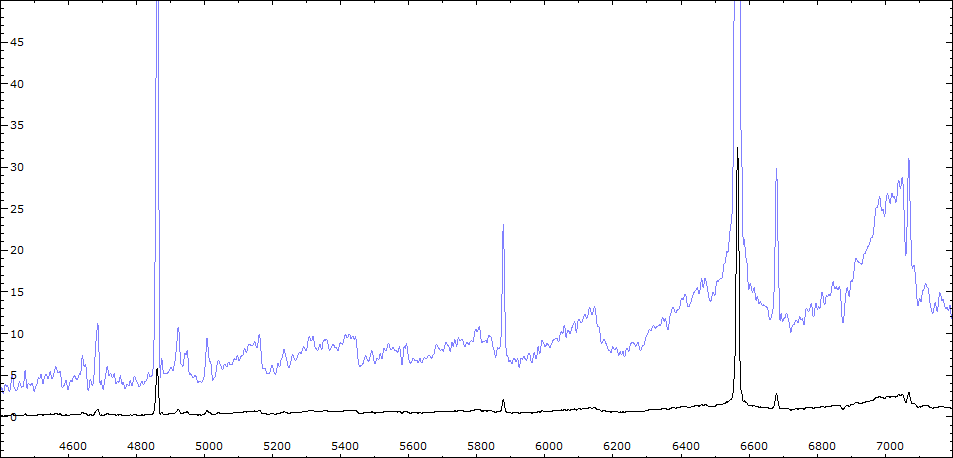
Line IdentificationSpectroscopy
Periodic variationsLes raies d'émission HI et HeI sont corrélées avec la phase photométrique et montrent un maximum vers la phase 0. Fe II 5169 atteint son intensité maximum également vers phase 0.
La raie de forte ionisation He II 4686 ne montre pas de variation significative, de même que les raies interdites [OIII] 5007 et 4363, [NeIII] 3869.
La raie de forte excitation [Fe VI]5176 varie de façon aléatoire.Les indices [TiO]1 (0.38 à 0.55) et [TiO]2 (0.8 à 0.95)suivent les variations photométriques - le maximum se situe vers la phase 0.5 - ce comportement peut être interprété de deux façons : 1) le composant chaud masque les bandes d'absortion de la géante rouge 2) ou provoque une variation du type spectral par réchauffement d'une face de la géante rouge.
Ces résultats montrent qu'il existe deux zones distinctes d'émission :
1- Zone de faible excitation, en phase avec les variations photométriques
2- Zone de forte excitation, indépendante de la phaseI(Ha)/I(Hb) = 5.1 +/- 0.2 I(Hg)/I(Hb) = 0.4 +/- 0.01 I(Hd)/I(Hg) = 0.24 +/-0.24
Extinction E B-V = 0.15
Hot component Cool Component M5.1 III (+/- 0.4) Kenyon & Fernandez-Castro 1987
M4.9 à M5.5 III Keyes& Preblish 2004
M4.5 III Murset 1999Nébuleuse Te = 15 à 20 000 K Ephemeris Max (U) = JD 2445125 (40) + 598 (29) x E
Max = JD 2450197 + 594 x EDobrzycka 1993
Fekel & al. 2000Outbursts Stable ____ Observations 2013 ____________________________________________________________________________________________
Date UT JD Telescope Spectrograph Slit R CCD Exp Phase Mag
____ Observations 2011 ____________________________________________________________________________________________
Date UT JD Telescope Spectrograph Slit R CCD Exp Phase Mag ____ Observations 2010 ____________________________________________________________________________________________
Date Heure TU Exp
Date Heure TU Exp
Date Heure TU Exp
Date Heure TU Exp
Date Heure TU Exp
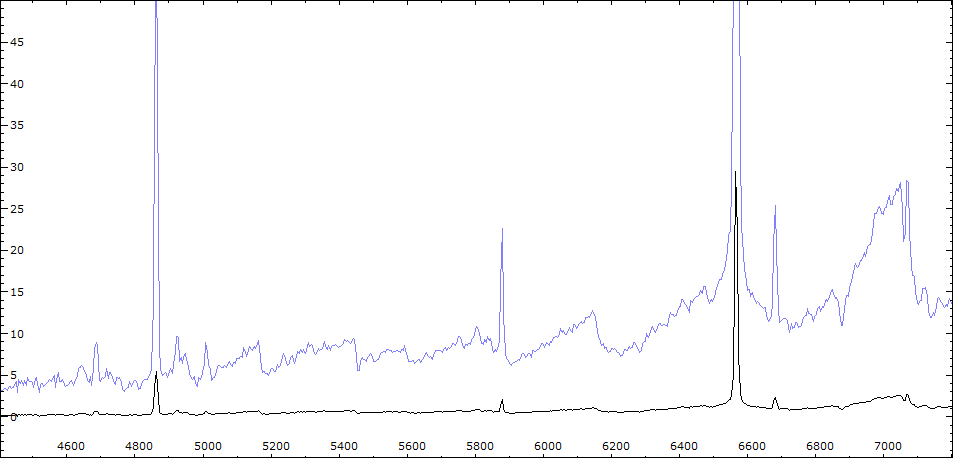
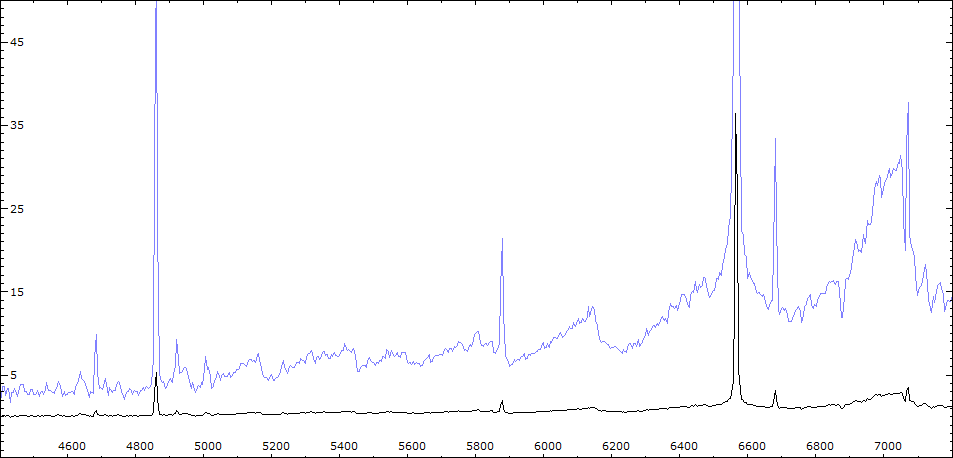
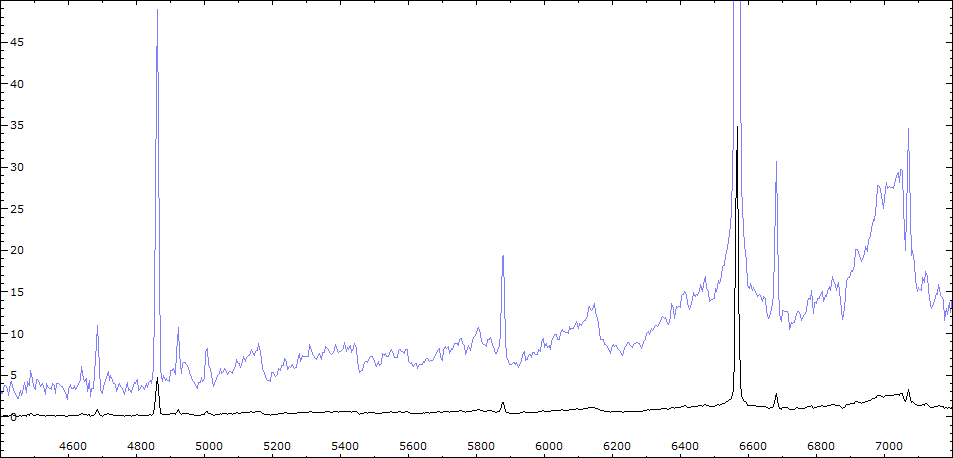
Comparaison Spectres V443 Her et FS Com (M5III)
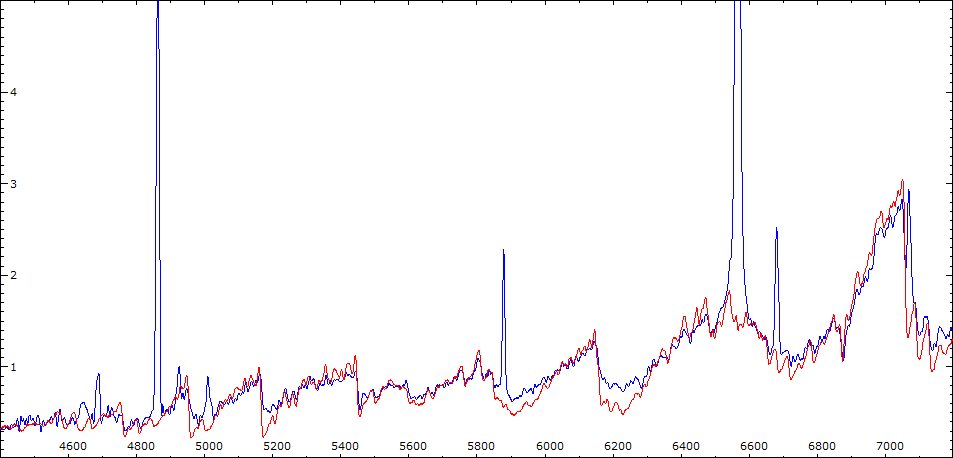
Comparaison spectres du 7/06/2010 et du 11/06/2010

Lines measurement in Dobrzycka & al. 1993
Publications
1984PASAu...5..369A
Proc. Astron. Soc. Australia, 5, 369-421 (1984)
A catalogue of symbiotic stars.
ALLEN D.A.1987AJ.....93..938K
Astron. J., 93, 938-949 (1987)
The cool components of symbiotic stars. I. Optical spectral types.
KENYON S.J. and FERNANDEZ-CASTRO T.1993AJ....106..284D
Astron. J., 106, 284-297 (1993)
Spectroscopic observations of V443 Herculis: a symbiotic binary with a low mass white dwarf.
DOBRZYCKA D., KENYON S.J. and MIKOLAJEWSKA J.1996Ap&SS.238..285S
Astrophys. Space Sci., 238, 285-302 (1996)
Circumstellar material in the symbiotic binary V443 Herculis.
SKOPAL A.1999A&AS..137..473M
Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser., 137, 473-493 (1999)
Spectral classification of the cool giants in symbiotic systems.
MUERSET U. and SCHMID H.M.2000A&AS..146..407B
Astron. Astrophys., Suppl. Ser., 146, 407-435 (2000)
A catalogue of symbiotic stars.
BELCZYNSKI K., MIKOLAJEWSKA J., MUNARI U., IVISON R.J. and FRIEDJUNG M.2004AJ....128.2981K
Astron. J., 128, 2981-2987 (2004)
Spectral and luminosity classification of symbiotic star cool components with near-infrared photometry.
KEYES C.D. and PREBLICH B.